06. Tree Classification
Common Tree Orders, Families, and Genera
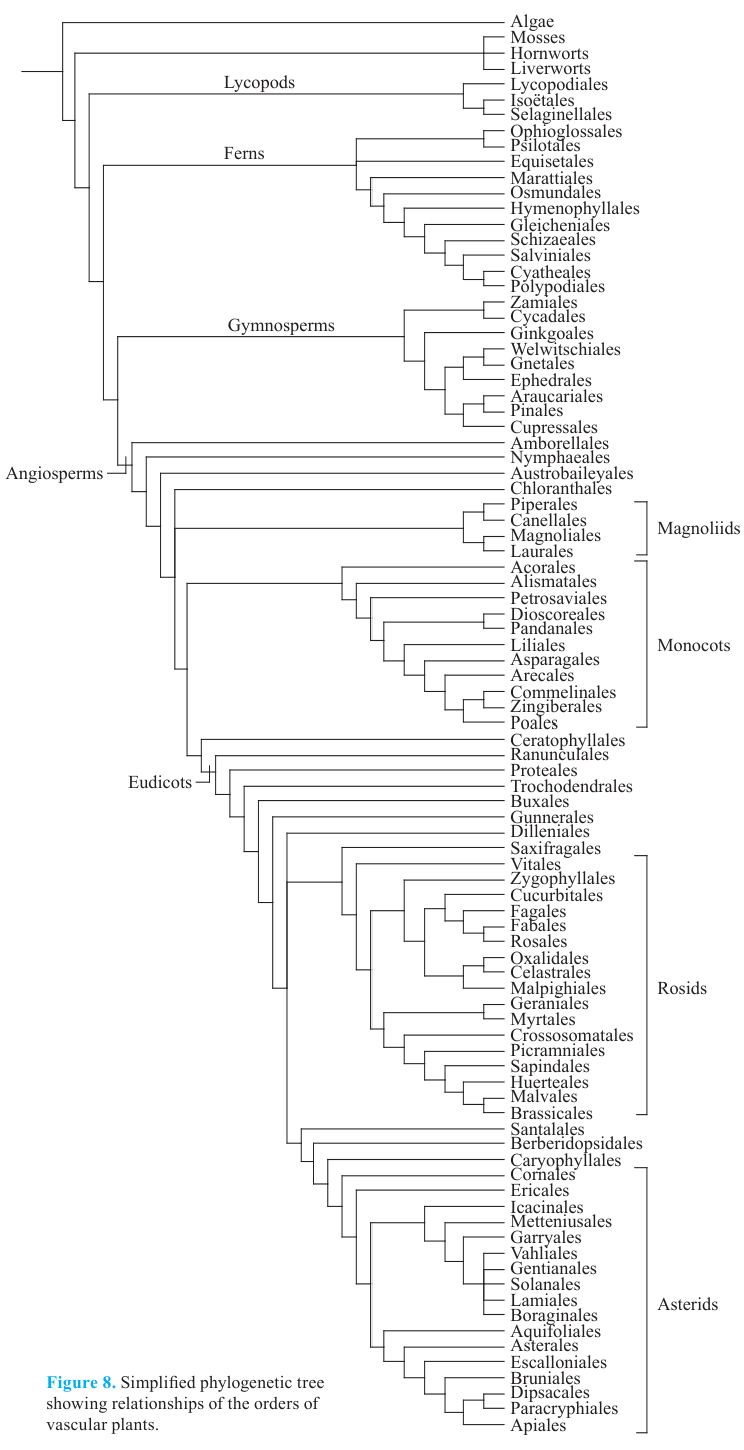
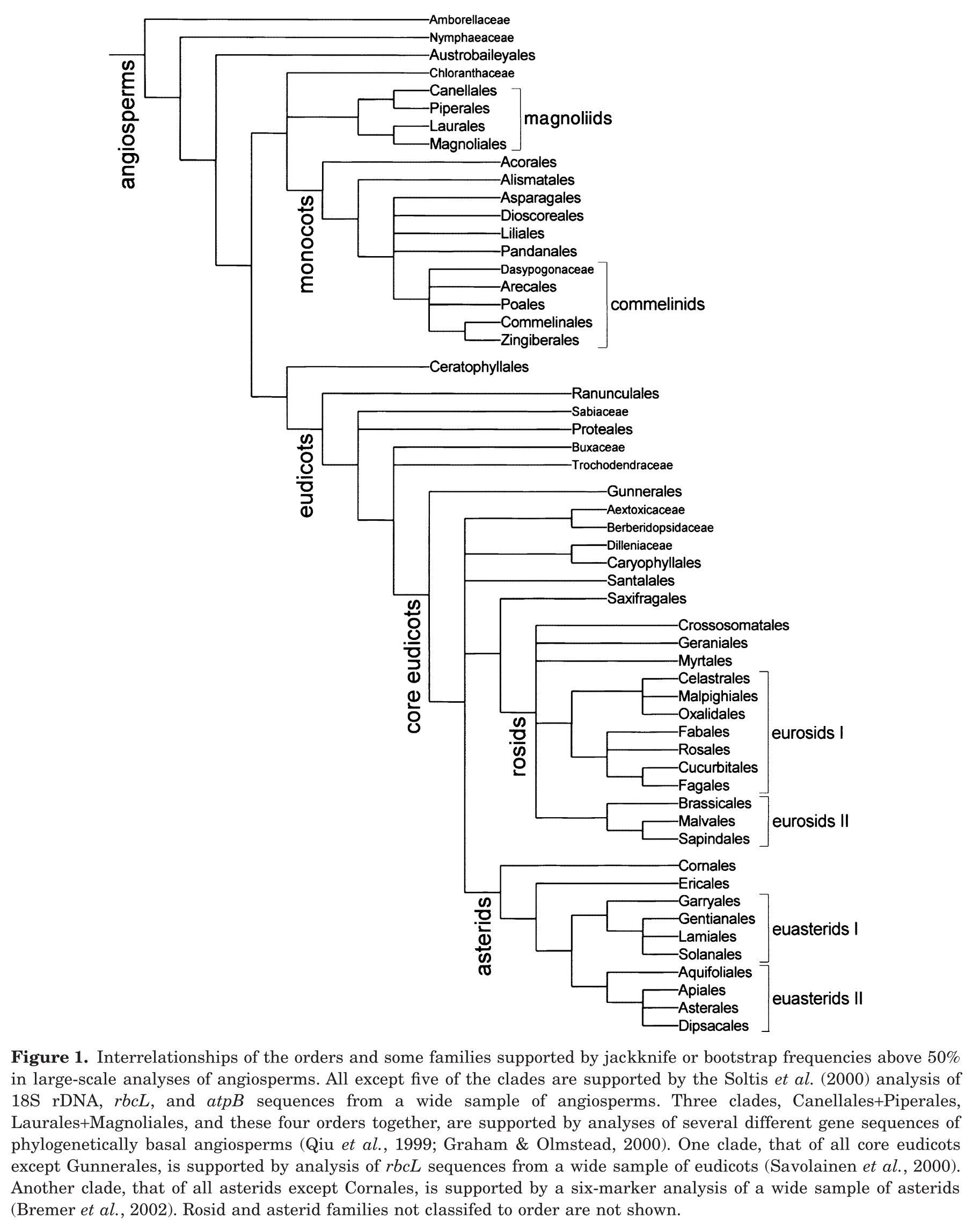
Trees are in the division Tracheophyta (vascular plants), which is divided into two major clades: Angiosperms (flowering plants) and Gymnosperms (non-flowering plants). The next two figures are helpful to provide context. Figure 1 shows the evolution of Tracheophyta down to orders and Figure 2 shows more detail for the Angiosperms.
Angiosperms (clade)
Angiosperms (clade) - Common Eudicots (class)
| Order (ales) | Family (aceae) | Genus |
|---|---|---|
| Aquifoliales | Aquifoliaceae | Ilex (Holly) |
| Fabales | Fabaceae | Robinia (Locust) |
| Fagales | Betulaceae | Alnus (Alder) |
| Fagales | Betulaceae | Betula (Birch) |
| Fagales | Betulaceae | Corylus (Hazel) |
| Fagales | Fagaceae | Fagus (Beech) |
| Fagales | Fagaceae | Quercus (Oak) |
| Fagales | Juglandaceae | Pterocarya (Wingnut) |
| Fagales | Ulmaceae | Ulmus (Elm) |
| Lamiales | Oleaceae | Fraxinus (Ash) |
| Malpighiales | Salicaceae | Populus (Aspen) |
| Malvales | Malvaceae | Tilia (Lime, Linden) |
| Rosales | Rosaceae | Crataegus (Hawthorn) |
| Rosales | Rosaceae | Malus (Apple) |
| Rosales | Rosaceae | Prunus (Cherry) |
| Rosales | Rosaceae | Rosa (Rose) |
| Rosales | Rosaceae | Sorbus (Rowan) |
| Rosales | Moraceae | Morus (Mulberry) |
| Rosales | Ulmaceae | Ulmus glabra, Ulmus procera, (Elm) |
| Rosales | Rhamnaceae | Rhamnus cathartica (Common Buckthorn) |
| Rosales | Rhamnaceae | Ziziphus (Jujube), non-UK |
| Rosales | Urticaceae | Celtis occidentalis (Common Hackberry, US) |
| Rosales | Cannabaceae | Humulus lupulus (Common Hop) non-tree |
| Rosales | Cannabaceae | Cannabis sativa (Hemp) cultivated |
| Rosales | Elaeagnaceae | Elaeagnus angustifolia (Russian Olive) non-UK |
| Sapindales | Juglandaceae | Juglans (Walnut) |
| Sapindales | Sapindaceae | Acer (Maple) |
The order Fabales, which includes nearly ten percent of eudicot diversity. The bulk of this is made up of Fabaceae, a dominant family in many ecosystems around the world. The order is well supported, although relationships among the families in the order are still disputed. The crown group is dated between 87 and 72 million years old (Christenhusz et al. 2020, p. 248).
Other Eudicots
Other Eudicots from Figure 1.
| Order | Common Tree Genera | Example Species |
|---|---|---|
| Apiales | Aralia, Schefflera | Aralia spinosa (Devil’s walking stick) |
| Aquifoliales | Ilex | Ilex aquifolium (Holly) |
| Asterales | Aster, Fraxinus | Fraxinus excelsior (European ash) |
| Brassicales | Carica, Moringa | Carica papaya (Papaya), Moringa oleifera (Drumstick tree) |
| Buxales | Buxus | Buxus sempervirens (Common box) |
| Cornales | Cornus | Cornus florida (Flowering dogwood) |
| Ericales | Arbutus, Rhododendron | Arbutus menziesii (Pacific madrone) |
| Fabales | Acacia, Robinia | Robinia pseudoacacia (Black locust) |
| Fagales | Quercus, Fagus, Betula | Quercus robur (English oak), Fagus sylvatica (European beech), Betula pendula (Silver birch) |
| Garryales | Garrya | Garrya elliptica (Coast silktassel) |
| Malpighiales | Salix, Populus | Salix alba (White willow), Populus tremula (European aspen) |
| Malvales | Tilia, Grewia | Tilia cordata (Small-leaved lime) |
| Myrtales | Eucalyptus, Lagerstroemia | Eucalyptus globulus (Blue gum) |
| Proteales | Platanus, Protea | Platanus occidentalis (American sycamore) |
| Ranunculales | Clematis, Aconitum | Clematis vitalba (Old man’s beard) |
| Rosales | Malus, Prunus, Ulmus | Malus domestica (Apple), Ulmus americana (American elm) |
| Sapindales | Acer, Aesculus | Acer saccharum (Sugar maple), Aesculus hippocastanum (Horse chestnut) |
| Saxifragales | Liquidambar, Hamamelis | Liquidambar styraciflua (Sweetgum) |
| Trochodendrales | Tetracentron, Trochodendron | Tetracentron sinense |
| Vitales | Vitis, Ampelopsis | Vitis vinifera (Common grapevine) |
Angiosperms (clade) - Magnoliids (clade)
| Order | Family | Genus |
|---|---|---|
| Magnoliales | Magnoliaceae | Magnolia (Magnolia) |
| Magnoliales | Magnoliaceae | Liriodendron (Tulip Tree) |
| Magnoliales | Myristicaceae | Myristica (Nutmeg) |
| Laurales | Lauraceae | Cinnamomum (Cinnamon, Camphor) |
| Laurales | Lauraceae | Persea (Avocado) |
Other Angiosperms
Other non-Eudicot Angiosperms from Figure 1.
| Order | Clade | Common Tree Genera | Example Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amborellales | Basal Angiosperms | Amborella | Amborella trichopoda (No common name, endemic to New Caledonia) |
| Nymphaeales | Basal Angiosperms | N/A (mostly aquatic plants) | N/A (Water lilies, not trees) |
| Austrobaileyales | Basal Angiosperms | Illicium | Illicium verum (Star anise) |
| Chloranthales | Basal Angiosperms | Chloranthus | Chloranthus japonicus |
| Piperales | Magnoliids | Piper, Peperomia | Piper nigrum (Black pepper) |
| Canellales | Magnoliids | Canella | Canella winterana (Wild cinnamon) |
| Magnoliales | Magnoliids | Magnolia, Liriodendron | Magnolia grandiflora (Southern magnolia), Liriodendron tulipifera (Tulip tree) |
| Laurales | Magnoliids | Cinnamomum, Persea | Cinnamomum verum (Ceylon cinnamon), Persea americana (Avocado) |
| Acorales | Monocots | Acorus | Acorus calamus (Sweet flag) |
| Alismatales | Monocots | Sagittaria | Sagittaria latifolia (Broadleaf arrowhead) |
| Petrosaviales | Monocots | N/A (no tree species) | N/A |
| Dioscoreales | Monocots | Dioscorea | Dioscorea alata (Purple yam) |
| Pandanales | Monocots | Pandanus | Pandanus tectorius (Screw pine) |
| Liliales | Monocots | Lilium, Smilax | Smilax rotundifolia (Roundleaf greenbrier) |
| Asparagales | Monocots | Agave, Yucca | Agave americana (Century plant), Yucca brevifolia (Joshua tree) |
| Arecales | Monocots | Phoenix, Cocos | Phoenix dactylifera (Date palm), Cocos nucifera (Coconut palm) |
| Commelinales | Monocots | Tradescantia | Tradescantia virginiana (Virginia spiderwort) |
| Zingiberales | Monocots | Musa, Zingiber | Musa acuminata (Banana), Zingiber officinale (Ginger) |
| Poales | Monocots | Zea, Bambusa | Zea mays (Maize), Bambusa vulgaris (Common bamboo) |
| Ceratophyllales | Basal Angiosperms | N/A (mostly aquatic plants) | N/A |
Remember that Magnoliids are an early-branching clade of angiosperms, often with aromatic compounds and large flowers, like Magnolia and Cinnamomum, and Monocots are a clade of angiosperms characterized by having a single cotyledon (seed leaf), parallel leaf venation, and floral parts in multiples of three, such as Palms (Arecales) and Bananas (Zingiberales).
Gymnosperms (clade)
Gymnosperms (clade) and Pinopsida (class)
| Order | Family | Genus |
|---|---|---|
| Araucariales | Araucariaceae | Araucaria (Monkey Puzzle) |
| Cupressales | Cupressaceae | Cupressus (Cypress) |
| Cupressales | Cupressaceae | Juniperus (Juniper) |
| Cupressales | Cupressaceae | Sequoia (Redwood) |
| Cupressales | Sciadopityaceae | Sciadopitys (Umbrella-pine) |
| Cupressales | Taxaceae | Taxus (Yew) |
| Pinales | Pinaceae | Abies (Fir) |
| Pinales | Pinaceae | Cedrus (Cedar) |
| Pinales | Pinaceae | Larix (Larch) |
| Pinales | Pinaceae | Picea (Spruce) |
| Pinales | Pinaceae | Pinus (Pine) |
| Pinales | Pinaceae | Tsuga (Hemlock) |
For example, the Cupressaceae family consist of 30 genera with c. 146 species: Arthrotaxis (3), Austrocedrus (1), Callitris (22), Callitrop- sis (1), Calocedrus (4), Chamaecyparis (5), Cryptomeria (1), Cunninghamia (2), Cupressus (9), Diselma (1), Fitzroya (1), Fokienia (1), Glyptostrobus (1), Hesperocyparis (16), Juniperus (c. 50), Libocedrus (5), Metasequoia (1), Microbiota (1), Papuacedrus (1), Pilgerodendron (1), Platycladus (1), Sequoia (1), Sequoiadendron (1), Taiwania (2), Taxodium (2), Tetraclinis (1), Thuja (5), Thujopsis (1), Widdringtonia (4) and Xanthocyparis (1) (Christenhusz et al. 2020, p. 84).
Gymnosperms (clade) and Ginkgoopsida (class)
| Order | Family | Genus |
|---|---|---|
| Ginkgoales | Ginkgoaceae | Ginkgo (Maidenhair tree) |
This class includes the order Ginkgoales, with the sole surviving family Ginkgoaceae and genus Ginkgo, represented today by the species Ginkgo biloba. All other species within Ginkgoopsida are extinct, making this a unique group with only one living member.
Other Gymnosperms
Figure 1 shows other Gymnosperms as follows.
| Order | Common Tree Genera | Example Species |
|---|---|---|
| Zamiales | Zamia, Lepidozamia | Zamia integrifolia (Coontie), Lepidozamia peroffskyana (Pineapple Zamia) |
| Cycadales | Cycas, Dioon | Cycas revoluta (Sago palm), Dioon edule |
| Ginkgoales | Ginkgo | Ginkgo biloba (Maidenhair tree) |
| Welwitschiales | Welwitschia | Welwitschia mirabilis (Welwitschia) |
| Gnetales | Gnetum | Gnetum gnemon (Melinjo) |
| Ephedrales | Ephedra | Ephedra sinica (Ma Huang) |
| Araucariales | Araucaria, Agathis | Araucaria araucana (Monkey Puzzle tree), Agathis australis (Kauri tree) |
| Pinales | Pinus, Abies, Picea | Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine), Abies alba (Silver fir), Picea abies (Norway spruce) |
| Cupressales | Cupressus, Juniperus, Sequoia | Cupressus sempervirens (Mediterranean cypress), Juniperus communis (Common juniper), Sequoia sempervirens (Coast redwood) |
Older Terminology and Modern Updates
The class Magnoliopsida in traditional taxonomy corresponds to a class of dicots that includes both Eudicots and Magnoliids.
In modern plant taxonomy, both Eudicots and Magnoliids are considered distinct clades rather than formal taxonomic classes. This shift is based on evolutionary relationships discovered through molecular phylogenetics. So, while Magnoliopsida was historically a class in older systems like the Cronquist system, today these groups are viewed as separate evolutionary lineages (clades), with Eudicots encompassing most “true dicots” and Magnoliids representing an early-branching group of flowering plants.
Other notable updates in the tables is the reclassification of Cupressaceae from Pinales to Cupressales in the gymnosperms. Otherwise, the eudicots, magnoliids, and monocots tables are largely stable, with only minor refinements at the family or subfamily level in some cases.